Routing
Important: These docs are for the outdated Jets 5 versions and below. For the latest Jets docs: docs.rubyonjets.com
Jets translates your routes.rb file into API Gateway resources, and connects them to your Lambda functions:
config/routes.rb:
Jets.application.routes.draw do
get "posts", to: "posts#index"
get "posts/new", to: "posts#new"
get "posts/:id", to: "posts#show"
post "posts", to: "posts#create"
get "posts/:id/edit", to: "posts#edit"
put "posts", to: "posts#update"
delete "posts", to: "posts#destroy"
resources :comments # expands to the RESTful routes above
any "posts/hot", to: "posts#hot" # GET, POST, PUT, etc request all work
end
You can check your routes in the API Gateway console:
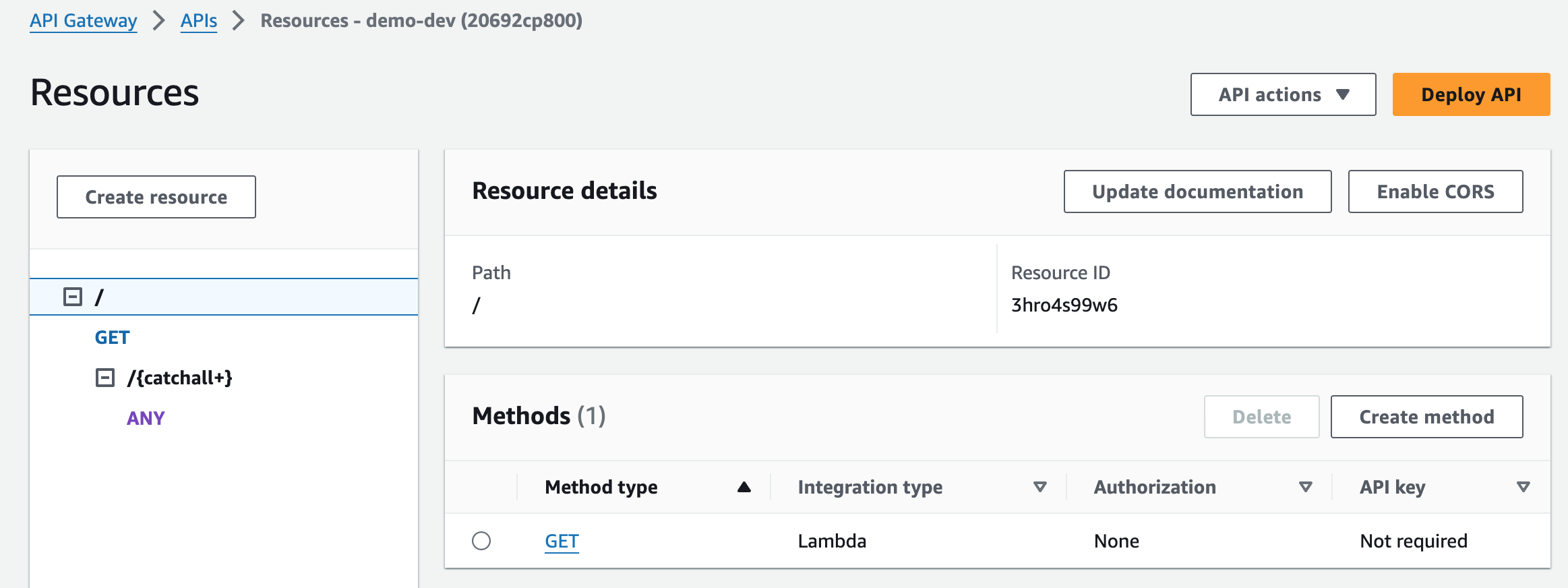
Note: In Jets v5, only the minimal APIGW Methods are created. APIGW essentially acts like a proxy to the Jets routing engine which is more flexible.
You can get your API Gateway endpoints from the API Gateway console, and test them with curl or postman. Example:
$ curl -s "https://quabepiu80.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/dev/posts" | jq .
{
"hello": "world",
"action": "index"
}
jets routes
Run the jets routes cli command to get a list of your routes.
$ jets routes
+-------------------+--------+--------------------+--------------------+
| As (Prefix) | Verb | Path (URI Pattern) | Controller#action |
+-------------------+--------+--------------------+--------------------+
| posts | GET | /posts | posts#index |
| posts | POST | /posts | posts#create |
| new_post | GET | /posts/new | posts#new |
| edit_post | GET | /posts/:id/edit | posts#edit |
| post | GET | /posts/:id | posts#show |
| post | PUT | /posts/:id | posts#update |
| post | PATCH | /posts/:id | posts#update |
| post | DELETE | /posts/:id | posts#destroy |
+-------------------+--------+--------------------+--------------------+
Routing Guide
There is more information about the Jets Router in the Routing Guide docs.
Production Deployment
Important: If you are deploying a production service, it is strongly recommended to use a Custom Domain. Jets computes and figures out whether or not it needs to replace the REST API as part of deployment. When the REST API is replaced, the API Endpoint will be different. By using Custom Domain, you’ll be able to keep the same endpoint.